What is page indexing
Website indexing is a process where a search engine bot visits you, tries to go through all the content, and stores it in its database (indexes it). When you search for "something" using a search engine, it doesn't start searching the entire internet. The search engine looks in its database and offers you relevant results for your query - so the pages in the search result must be indexed by it. If the search engine doesn't have them stored in its database, it's clear that it won't display them. You can think of the database as a kind of library of websites from which the search engine finds the best answer to the searched query. Therefore, it is important to focus on website indexing in search engines for every project.
Poor website indexing
As usual, with websites, it is possible that search engines don't know about all the pages you want to display in search results. Then you can lose visitors and may not cover a segment that is beneficial for your business. Imagine, for example, that you might not have your main page, e-shop category, blog articles, etc., in the search engine index. And if the search engine doesn't have them stored in its database, it can't display them in search results.
Many websites commonly use non-indexing of pages - you don't want to display pages in search results. It can be, for example, thank you pages, an e-shop cart, user sections, and much more.
However, sometimes you want to index a page, you send the page URL to search engines for their crawling bot to evaluate. You might have it in a sitemap or even manually send it for indexing - "Add Page" on Seznam and "Submit URL" on Google. However, it can happen that the search engine may decide not to index it anyway. Then it is important to find out what might be the reason why the search engine doesn't want to display it and what prevents it from indexing.
Analysis of website indexing
There are many ways to check the status of indexed pages. Look at the basic steps I follow.
Checking page indexing using the site operator
I tried to generally write a guide on how you can also check the status of indexing your websites. Since this question was asked quite often, I created an answer to it in the SEO clinic, where you can also find other SEO tips. It's mainly about comparing the number of URLs you want to display in search results with the number of pages returned using the site operator.
Checking page indexing using sitemap and Marketing Miner
If you have created a sitemap with URLs that you want to display in search results, we can specifically find out which pages are being indexed and possibly those that are not displayed in the search. First, before checking the display of pages, see if your sitemap really only contains URLs that you want to send to search results.
For the actual analysis of the pages sent through the sitemap, I use Marketing Miner, which contains a useful Fulltext Index Checker function.
- Go to the Marketing Miner website and log in
- Choose that you want to create a "New report"
- To the question of what query you want to insert, choose "URL"
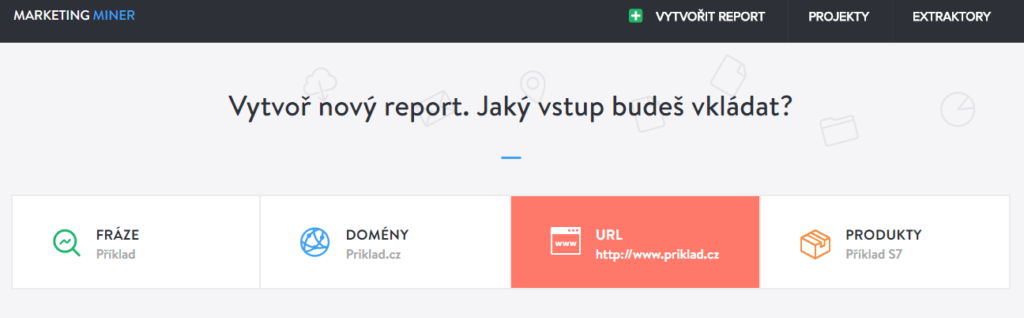
- Choose "Sitemap / RSS" and enter the sitemap URL, you can rename the report and choose "Go to miners"
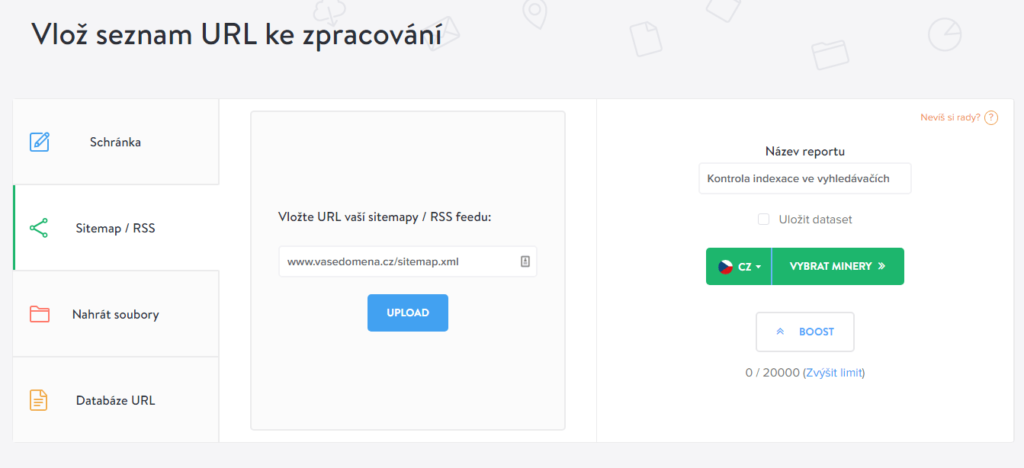
- Choose the Fulltext Index Checker among the miners
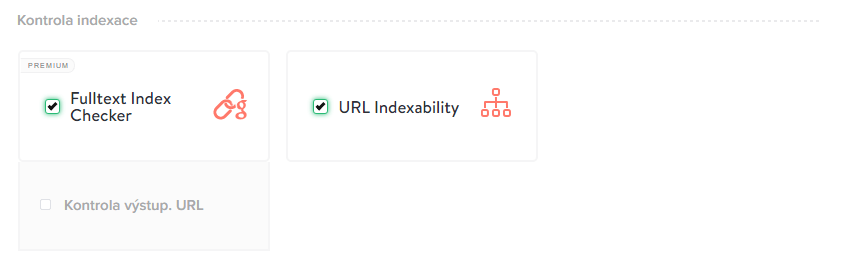
TIP: You can also choose URL Indexability - you will find out which URLs are indexable, which are canonicalized, or which are prohibited in robots.txt
Marketing Miner will show you which URLs are indexed and which are not. In my opinion, this is the fastest and simplest way to create a quality analysis of page indexing.
Checking page indexing, for example, using Google Analytics or Google Data Studio
In general, but not exactly, you can also determine page indexing through landing pages - from organic search. You can filter landing pages directly in the Google Analytics analytical tool, or you can create your own overview using Google Data Studio. Just download the reports for a certain period and compare them with the URLs sent in the sitemap.
If there was traffic on the landing pages from search engines, then they logically appear in search results. And if the traffic is zero, then it's worth checking why.
Why might pages not appear in search?
There can be several reasons why web pages do not appear in search results. Sometimes the cause can be visible at first glance, but sometimes you have to focus more deeply on the issue of poorly indexing pages.
- Check if the page contains a meta tag with the "noindex" parameter - used to prohibit page indexing.
- Check if the page is blocked through robots.txt (even via robots.txt it is possible to disable indexing of pages, but this file should not be used for this purpose).
- Check if the page has a simple URL that is not obstructing indexing for search engines (hashtags in URL, parametric URLs)
- Is the page internally linked and leads to a working link?
- Are there any redirects on the target URL? Or are there many of them?
- Is the page listed in the sitemap?
- Isn't the page duplicate to an already created page on your website? Does the search engine have a reason to also display it in search results?
- Page quality or penalty (see below)
TIP: Support the page by linking it with backlinks. There can be many more reasons, but these are the most common causes I encounter.
Page usefulness - is the page beneficial for users?
If the page is not indexed, even though it has all the prerequisites to be indexed, then another option is to check the content of the page. In addition to not being duplicate with another page, see if the page content is useful for users. If so, then check if you are linking to relevant websites (outgoing links), if you don't have a lot of generated texts on the page, if you don't display different content to search engines than to users, and other possible shortcomings that could bother search engines.
Once I also encountered that websites used article ratings, but this rating was generated - so it was not added by the user himself. Google then penalized the website for these pages and stopped displaying them.
Penalties
The worst case that can happen is a penalty. You can find out about a possible manual penalty directly in Google Search Console, then in the "Manual Actions" section.
It can also happen that you have malware on your pages. You can then find it in GSC in the "Security Issues" section.
How to quickly index newly created pages
If you want to quickly index the content of your websites, there are procedures to speed up indexing. If you create a page that you want to display in search results, then:
- send the page manually for indexing
- have the page in the sitemap, which you send through services
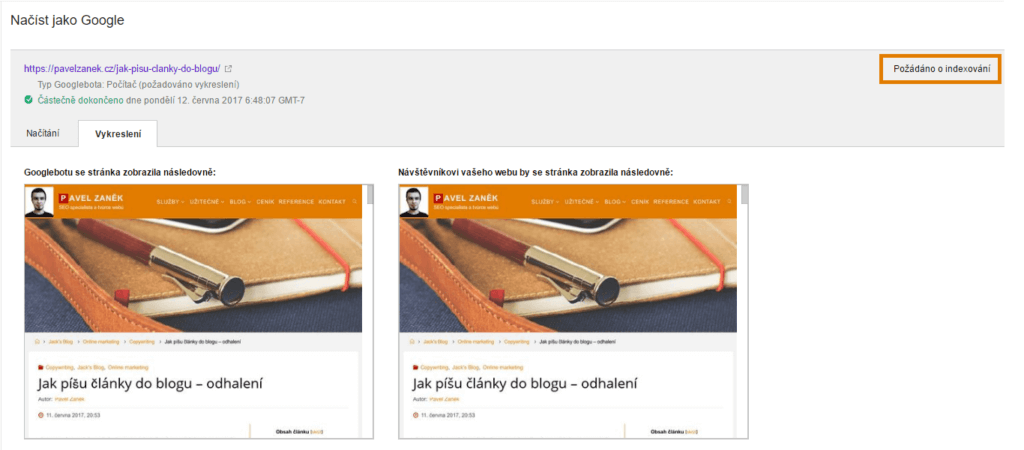
In Google Webmaster Tools (Google Search Console), you can also use another function - Fetch as Google. Through the tool, you request a rendering of the web page, and if no problem is found, you can immediately request page indexing. For example, you can find out which resources Googlebot couldn't download.
In conclusion
There can be several reasons why a page may not be indexed correctly. However, make pages primarily for users and not for search engines. Then pay attention to other technical prerequisites that search engines expect and you won't cause them problems. If you decide to use the noindex parameter somewhere, then check the changes made. There is nothing worse than deindexing pages and then losing traffic.